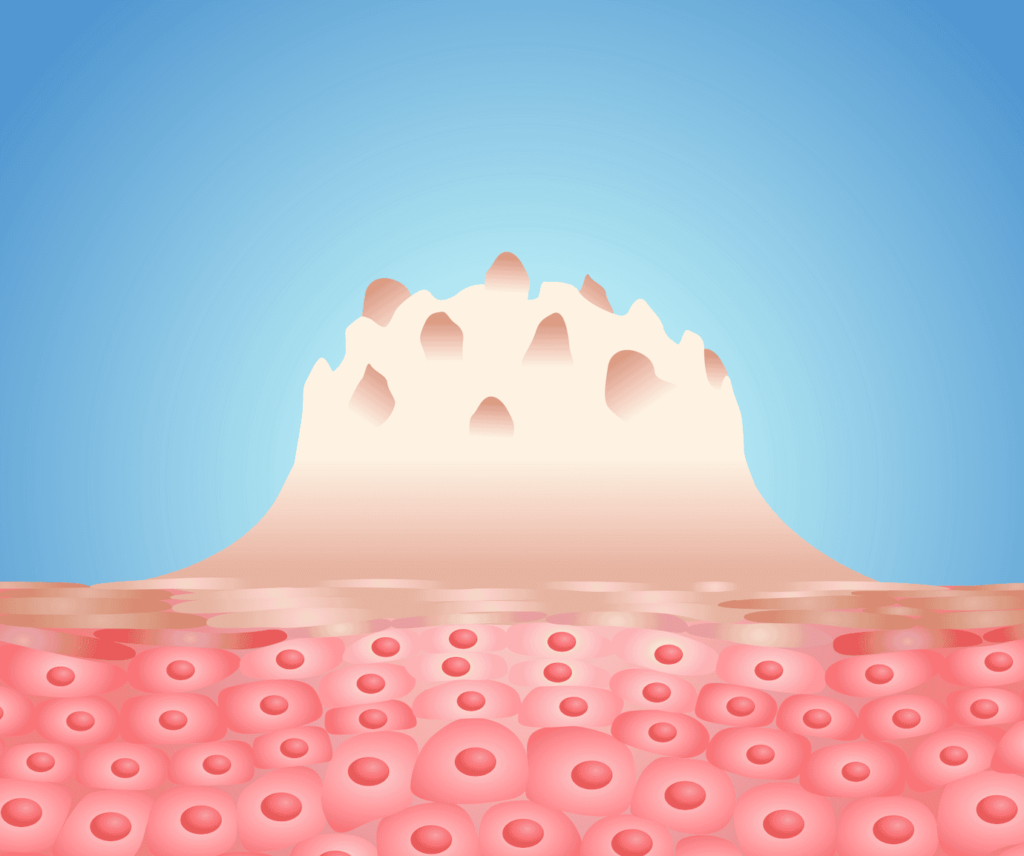
Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV).
This disease often appears in the form of small and soft warts on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital area and anus.
There are many types of HPV, but some types, including HPV 6 and HPV 11, are responsible for most genital warts.
Some other types of HPV can be linked to genital cancers (such as cervical cancer), but genital warts are not usually cancerous.
Symptoms of genital warts
Genital warts may not cause symptoms and appear only as small and soft growths on the skin. But sometimes the following symptoms are seen in people:
1. Visible warts: These warts are usually soft lumps that are the same color or darker than the skin and may be seen in the genital area,
anus, or even the mouth and throat (if transmitted through oral sex).
2. Itching or burning: Some people may feel itching, burning or discomfort in the area where the warts are.
3. Bleeding: In some cases, warts may bleed, especially if they are irritated or scratched.
Ways of transmission of genital warts
HPV is usually transmitted through direct contact with infected skin and mucous membranes. The main ways of transmission of this virus are:
1. Sex: Genital warts are transmitted through sexual contact (vaginal, anal and oral).
2. Skin-to-skin contact: Even if there is no full sex, the virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact.
3. Transmission from mother to baby: In rare cases, the virus may be transmitted from mother to baby during natural childbirth and warts may develop in the baby’s mouth or throat.
Prevention of genital warts
To prevent genital warts and the HPV virus, you can do the following:
1. Vaccination: HPV vaccine (such as Gardasil and Cervarix) can prevent high-risk types and some types that cause genital warts.
These vaccines are usually recommended for young people before they become sexually active.
2. Condom use: Although condoms do not completely prevent HPV transmission, they can reduce the risk.
3. Having protected sexual relations: reducing the number of sexual partners and observing sexual hygiene can be effective in reducing the risk of HPV infection.
Treatment of genital warts
Genital warts usually heal on their own over time, but some people need treatment to reduce discomfort and prevent transmission. Treatment methods include the following:
1. Topical medications: Medications such as podophyllin and imiquimod are applied directly to the warts.
2. Cryotherapy (Cryotherapy): This method freezes the warts and destroys them using liquid nitrogen.
3. Laser therapy: Laser is used to remove warts in more severe cases.
4. Surgery: In cases where the warts are large and stubborn, the doctor may use surgery to remove the warts.
The importance of diagnosis and follow-up
Although genital warts are not usually cancerous, some types of HPV can increase the risk of cervical cancer and other genital cancers.
Therefore, especially in women, it is very important to perform Pap smear test and periodic examinations.
These examinations can prevent the occurrence of more serious complications and, if necessary, begin appropriate treatments.
Important points
• Not sharing personal items: To reduce the risk of virus transmission, avoid sharing personal items such as towels and underwear.
• Observing personal and sexual hygiene: Observing hygiene and washing hands after contact with warts can prevent the transmission of the virus to other parts of the body.
• Open relationship and consultation with a doctor: If you see genital warts or any unusual changes in the genital area, you should see a doctor and get advice.
conclusion
Genital warts are a common and infectious disease that is transmitted through the HPV virus.
Although this disease is usually not dangerous, it is necessary for patients to see a doctor and use proper prevention methods to avoid transmission and possible complications.
Vaccination and sexual hygiene are among the best ways to reduce the risk of HPV and genital warts.

The role of vaccination in the prevention of genital warts and HPV-related cancers
HPV vaccines such as Gardasil and Cervarix are known as one of the most effective methods of preventing dangerous types of HPV virus.
These vaccines are designed to prevent infections caused by certain types of HPV that cause genital warts and some cancers such as cervical cancer, anal cancer, and even oral and throat cancers.
The HPV vaccine has the best effect when it is injected before starting sexual activities; For this reason,
many health organizations recommend that this vaccine be administered to adolescents (usually between the ages of 9 and 12).
The effect of genital warts on the psyche and social relations
Having genital warts may affect people’s mental health and social relationships.
Many people are embarrassed to express their problem due to shame, worry or fear of rejection and may refuse to go to the doctor and receive treatment.
This can lead to isolation, anxiety and even depression.
In addition, genital warts can negatively affect emotional and marital relationships;
As a result, having an open and honest relationship with a life partner and receiving emotional support can help in reducing psychological pressure and better management of the disease.
The importance of periodic examinations and screening
The HPV virus may exist in the body without specific symptoms; Therefore, even people who do not have visible genital warts may be carriers of the virus.
For this reason, periodic examinations and screenings, especially Pap smear tests for women, are very important.
This test can detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix and, if necessary, take faster treatment.
In some cases, the doctor may also recommend an HPV test for people who are at higher risk because of their sexual activities.
The importance of public awareness and education about HPV and genital warts
Public awareness and education about HPV and genital warts can help reduce taboos and increase public awareness of this disease.
Many people mistakenly believe that genital warts are a sign of misconduct due to insufficient information, misconceptions, or societal judgments.
Increasing education and information can help people to deal with this disease as a treatable health problem and act with more awareness of prevention methods.
summary
Genital warts are a common infection that can be transmitted through sexual contact, which can be prevented and controlled by observing sexual hygiene, vaccination and periodic examinations.
Affected people should get rid of social stigmas and care about their health instead of fear and embarrassment by visiting a doctor and receiving proper treatment.
Finally, emotional and psychological support from the family and society can have a significant effect on improving the mental and physical condition of people suffering from this disease.
The effect of genital warts on reproductive health
HPV and genital warts by themselves usually do not directly affect fertility, and infected people can become pregnant naturally.
However, in cases where HPV causes precancerous changes in the cervix, treatments such as removal of abnormal cells (laser therapy, cryotherapy, or conization) may be needed.
Some of these treatments can increase the chance of premature birth or cervical problems in pregnancy.
Therefore, if a person with HPV or genital warts is planning to get pregnant, it is better to consult with your doctor before getting pregnant so that any necessary treatment can be done in time.
The impact of the HPV virus on pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body’s immune system may change and thus, genital warts grow more in some pregnant women.
In most cases, warts go back to normal after delivery without any special treatment.
However, if the warts grow large enough to block the birth canal, your doctor may recommend a cesarean section.
Also, in rare cases, the HPV virus may be transmitted to the baby through natural childbirth.
If this happens, the baby may be infected with a type of HPV that causes warts in the respiratory tract (respiratory papillomatosis).
Although this condition is rare, because of its potential, doctors may consider delivery options for patients with HPV.
Treatment and management of genital warts during pregnancy
Many treatments for genital warts are not recommended during pregnancy because they may harm the fetus.
However, if the warts are very large and uncomfortable, your doctor may use safer methods such as cryotherapy or trichloroacetic acid.
The best treatment decision for pregnant women is usually determined according to the individual’s specific conditions and the doctor’s opinion.
The importance of a frank and transparent conversation with a life partner
In cases where a person has genital warts, it is very important to have a frank and transparent conversation with the partner.
The life partner should be aware of the person’s condition so that they can use appropriate prevention methods together.
Some people may feel embarrassed to talk about this, but transparency and communication can help build trust and mutual support.

Community resources and supports for people with genital warts
Many people with genital warts may feel that they are alone or that the problem isolates them from others.
This is where the role of social support resources, such as support groups or professional counseling, is invaluable.
Such groups and counseling can provide adequate information about the disease, prevention methods, and mental health management strategies.
In this way, affected people can share their feelings and concerns with others and find solutions to cope with the challenges related to this disease.
Final summary
Genital warts and HPV infection are common and preventable diseases that, if diagnosed early and properly managed, will not have much impact on the quality of life and health of people.
Being aware of the disease, taking care of yourself and seeing a doctor on time can help people to reduce their worries and continue to live a healthy and active life.
Social support, public education and receiving correct and scientific information from reliable sources also play an important role in reducing the stress
and psychological pressure of patients with genital warts.
Finally, paying attention to the importance of sexual health and talking about it in society can help reduce cases and increase public awareness and lead to a healthier and more informed society.
The importance of mental health in the management of genital warts
Having genital warts can have a huge impact on people’s mental health, especially due to social judgments and feelings of shame.
Feelings of anxiety, depression and low self-confidence are common among sufferers.
To deal with these challenges, psychological support and counseling from mental health professionals can help patients cope with this disease better.
Psychotherapy techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help patients manage their negative thoughts and worries.
Public awareness and information as a way to reduce taboos
Genital warts and HPV infection are still associated with social taboos in many societies.
For this reason, public information and health education can help reduce these taboos and change society’s attitude towards sexually transmitted diseases.
Creating educational programs in schools and health centers, providing educational content in the media,
and creating an open space for discussing sexual and health issues can help people become more aware of their health and prevent diseases.
The role of the family in support and empathy
Family and relatives can play a very important role in reducing the stress and anxiety of patients. Emotional family support,
acceptance of the disease and providing psychological help can help people not feel isolated and more easily cope with the challenges caused by genital warts.
Families can encourage the affected person to take care of themselves and pursue treatment by treating them positively and sympathetically and avoiding judgment.
Legal protections and health policies for people with genital warts
One of the effective measures to support people with genital warts and HPV is to create health policies and protective laws.
Providing easy and free access to the HPV vaccine, conducting free screenings,
and providing facilities for the treatment of this disease can help reduce the spread of the disease and prevent its complications.
Also, creating working and educational environments in which sufficient attention is given to the sexual health of people can reduce the social stigma that sufferers of this disease may experience.
The role of doctors and health professionals in raising awareness
Doctors and medical staff are at the forefront of awareness and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases.
Providing correct information to patients and raising awareness about prevention, treatment and personal care methods can help reduce the prevalence of genital warts.
Doctors can encourage patients to use vaccinations, perform periodic screenings, and take appropriate treatment strategies if they develop the disease.
HPV infection prevention training in teenagers and young adults
Teaching to prevent HPV infection and genital warts from a young age can help reduce the rate of infection in young people and adults.
Teaching sexual health in schools and providing information about the importance of vaccination
and the use of protective methods such as condoms are among the measures that can help prevent this disease.
Adolescent awareness of these issues can encourage them to make more informed choices and more protected behaviors in the future.
The final message
Genital warts and HPV virus, although it may be a threat to physical and mental health, but by following health tips, receiving vaccines,
and performing periodic examinations, its complications and spread can be prevented.
Society can also provide a safer and healthier environment for everyone by supporting patients, reducing social taboos and promoting public awareness.
Having the right information and getting social support are the first steps to managing this disease and living a healthier life.