Uterine fibroids, also called myomas or leiomyomas, are noncancerous (benign) lumps that grow in the wall of the uterus.
These masses are composed of muscle tissue and fibrosis and are usually seen in women of reproductive age.
Fibroids can appear single or multiple in the uterus, and their size can vary from a few millimeters to a few centimeters.
Most fibroids are asymptomatic, but some can cause discomfort and complications.
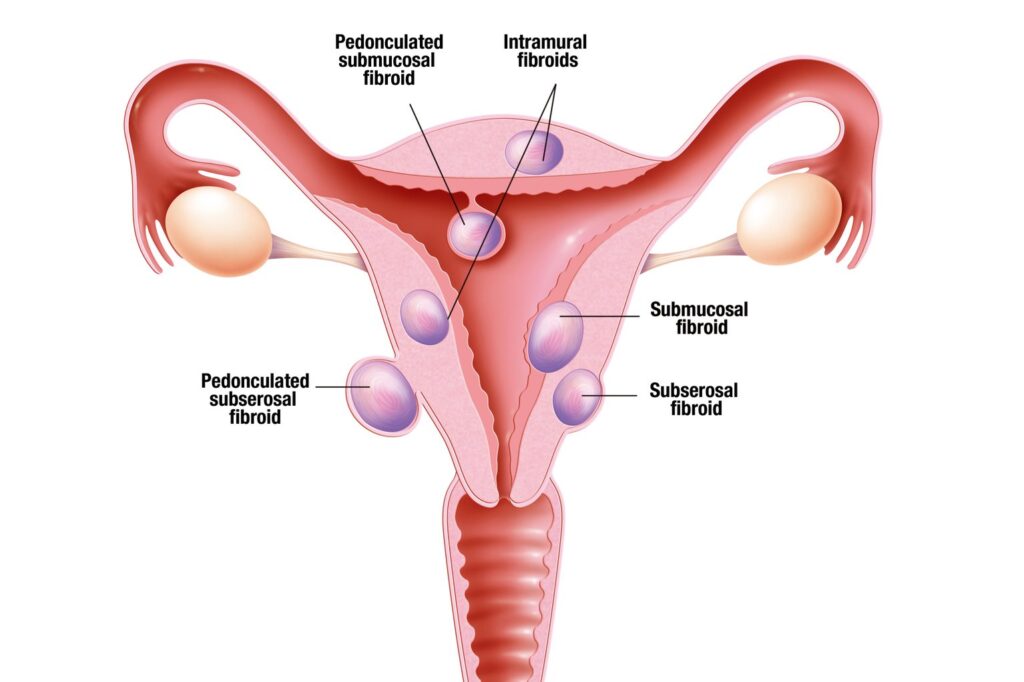
Types of uterine fibroids
According to their location in the uterus, fibroids are divided into four main types:
1. Submucosal fibroids: These types of fibroids grow in the inner layer of the uterus (under the lining of the uterus) and can protrude into the uterine cavity.
This type of fibroid causes abnormal uterine bleeding.
2. Wall fibroids: These fibroids grow in the muscle layer of the uterus (myometrium) and may cause the uterus to enlarge. These types of fibroids can cause pelvic pain and a feeling of pressure.
3. Subperitoneal fibroids: These fibroids grow in the outer layer of the uterus (under the peritoneal layer) and may protrude towards the abdominal cavity.
This type of fibroid is usually asymptomatic, but if it grows, it can put pressure on other organs.
4. Pedicled fibroids: These fibroids are attached to the uterus by a stalk and may cause severe pain due to the rotation of their stalk.
Causes of uterine fibroids
The exact cause of fibroids is still not fully known, but some factors may play a role in their development:
• Hormones: The hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are secreted by the ovaries, can stimulate the growth of fibroids.
These hormones cause fibroids to enlarge by affecting the tissue of the uterus.
• Genetics: Fibroids may be more common in people who have a family history of it.
• Cell growth factors: Some chemicals in the body that help cells grow can be effective in the growth of fibroids.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
Most fibroids are asymptomatic and are discovered incidentally during tests and examinations. But in cases where symptoms do occur, they may include the following:
1. Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding: Fibroids can cause heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding.
2. Bleeding between periods: In some cases, fibroids cause bleeding at times other than menstruation.
3. Pelvic and back pain: especially if the fibroids are large and press on other organs.
4. Urinary pressure and frequency: Large fibroids can put pressure on the bladder and increase the frequency of urination.
5. Pain during sex: In some cases, fibroids may cause pain during sex.
6. Digestive problems: The pressure of large fibroids may put pressure on the intestines and cause constipation.
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are usually diagnosed using the following methods:
• Pelvic examination: the doctor can detect the size or abnormality in the uterus by physical examination.
• Ultrasound: This imaging method with the help of sound waves can show the location and size of fibroids.
• MRI: In more complex cases, MRI is used to see the fibroids more closely and determine their location and number.
• Hysteroscopy: In this method, the doctor enters the uterine cavity through the vagina and cervix and examines the fibroids inside the uterus with a small camera.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
Treatment of uterine fibroids depends on the size, location, number and severity of symptoms. Some of the treatment methods include the following:
1. Drug treatment: Drugs such as hormones that regulate menstruation can help reduce symptoms.
Medicines that block the hormones estrogen and progesterone may also reduce the growth of fibroids.
2. Myomectomy surgery: In this method, the doctor removes the fibroids without removing the uterus. This method is more suitable for women who intend to get pregnant.
3. Hysterectomy: This surgery involves the complete removal of the uterus and is performed only when the fibroids are very large or painful and other treatments are not effective.
4. Uterine artery embolization: In this method, by closing the arteries feeding the fibroids, it reduces the blood flow to them and ultimately shrinks the fibroids.
5. Cryotherapy and laser: these methods are applied directly to fibroids and destroy them.

Prevention of uterine fibroids
Although there is no surefire way to prevent fibroids, following a healthy lifestyle can reduce your chances of developing them:
• Healthy diet: Eating foods rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and reducing red meat and saturated fats may be helpful.
• Regular physical activity: Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of fibroids.
• Stress management: Stress can affect hormones, and reducing stress can help control hormones.
Final remarks
Uterine fibroids are harmless in many cases and do not require treatment, but in case of annoying symptoms or causing problems in daily life,
it is better to see a doctor to choose the right treatment method.
By conducting regular examinations and having a healthy lifestyle, you can help control fibroids and prevent their possible complications.
One of the main concerns of women with uterine fibroids is the effect of these masses on fertility and pregnancy.
Although most fibroids do not affect fertility, in some cases, especially when the fibroids are large or located in certain positions of the uterus, they can cause fertility problems.
1. Submucosal fibroids: These types of fibroids can change the shape of the uterine cavity, prevent implantation of the fertilized egg or lead to abortion.
2. Effect on sperm and egg transfer: wall or large fibroids may prevent the transfer of sperm to the egg or the transfer of the egg to the uterus due to obstruction.
3. Pregnancy complications: Fibroids can be associated with an increased risk of premature birth, miscarriage, heavy bleeding during pregnancy and delivery problems.
It is important for women who are planning to get pregnant to be under the supervision of a doctor and, if necessary, take the necessary treatments before trying to get pregnant.
Treatments such as myomectomy, which removes fibroids without damaging the uterus, are recommended for people trying to get pregnant.
Management and control of symptoms of uterine fibroids
In cases where fibroids are asymptomatic or with mild symptoms, doctors may recommend monitoring rather than immediate treatment. Some symptom management methods include:
1. Pain control: Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help reduce pain.
2. Reducing menstrual bleeding: taking birth control pills or hormonal drugs can help regulate menstruation and reduce bleeding.
3. Dietary changes: Consuming iron-rich foods and iron supplements help prevent anemia from heavy bleeding.
The difference between fibroids and uterine cancer
Unlike cancerous tumors, uterine fibroids are benign masses and rarely turn into cancer.
Although fibroids do grow, this growth is often different from the uncontrolled growth of cancerous tumors, and fibroids do not spread to other tissues.
However, if you experience unusual symptoms such as heavy bleeding, persistent pain, or a change in your menstrual pattern,
it’s important to see your doctor to check for fibroids and any other changes.
Lifestyle and its effect on uterine fibroids
Lifestyle changes can help control the symptoms of fibroids and reduce the risk of their growth:
• Diet rich in fiber: Consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps improve overall health and lower estrogen levels in the body.
• Avoiding high consumption of alcohol and caffeine: high consumption of these substances may help to increase the level of estrogen and thus the growth of fibroids.
• Maintaining a healthy weight: obesity and overweight can increase the risk of fibroids by increasing the level of estrogen in the body.
• Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can balance the body’s hormone levels and help reduce the risk of fibroids.
Emotional and psychological support
Uterine fibroids can have effects on a person’s mental and emotional health. Heavy bleeding, frequent pain, and fertility concerns may cause anxiety, stress, and reduced quality of life.
Support from family, friends and counseling with a psychologist or counselor can help a person cope with these psychological problems.
Final remarks
Uterine fibroids are usually benign diseases and in many cases remain untreated.
However, if they cause symptoms or disrupt daily life, appropriate treatment methods can be used in consultation with a doctor.
By doing regular examinations and paying attention to your physical and mental health, you can manage this disease well and prevent possible complications.

The role of periodic examinations and medical care in the management of uterine fibroids
Periodic examinations and regular medical care play a very important role in identifying, monitoring and controlling uterine fibroids.
If fibroids are detected in the early stages, it is more likely to control symptoms and prevent their growth.
Doctors usually advise women to have regular checkups based on their age and symptoms. Methods of investigation and monitoring of fibroids include:
1. Regular ultrasounds: Especially for women who have large or multiple fibroids, periodic ultrasounds can monitor changes in the size and location of fibroids.
2. Blood tests: In case of severe bleeding, blood tests are necessary to diagnose and manage anemia.
3. Pap smear and related tests: Although the Pap smear does not specifically detect fibroids, this test is important for diagnosing other uterine problems
and can monitor the health of the reproductive system in general.
The effect of fibroids on the quality of life
Uterine fibroids, especially when they cause severe symptoms, may affect a person’s quality of life.
Heavy bleeding can cause anemia and extreme fatigue, and pelvic and back pain may also limit daily activities.
In the long run, these side effects can affect a person’s physical and mental health.
Some women may experience anxiety and worry due to concerns about fertility problems or the complications of fibroids.
To manage these effects, it is helpful to follow some tips:
• Medical and psychological counseling: Talking to a doctor and a psychological counselor can help a person cope with the worries and stress caused by the disease.
• Join support groups: Joining support groups can help share experiences with other women with fibroids and get emotional support.
• Attention to self-care: adequate rest, healthy nutrition and stress management help to improve the quality of life and reduce the complications of the disease.
The role of nutrition in the management of uterine fibroids
Healthy eating can be effective in controlling fibroids and reducing their symptoms. Some research suggests that certain foods may help slow the growth of fibroids or manage their symptoms:
1. Dietary fibers: Eating high-fiber foods such as green leafy vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can help regulate estrogen levels.
2. Foods rich in antioxidants: Antioxidants can protect the body’s cells from damage, and consuming foods such as berries, green tea, and nuts is helpful.
3. Healthy fats: Consuming unsaturated fats such as olive oil and fatty fish helps reduce inflammation and hormonal balance.
4. Reducing consumption of sugar and saturated fats: High consumption of sugar and saturated fats may increase estrogen levels and growth of fibroids.
Home care to reduce the symptoms of uterine fibroids
In addition to treatment methods, some home care can also help reduce the symptoms of fibroids:
• Warm compress: Using a warm compress on the abdomen can help reduce the pain caused by fibroids.
• Exercise and physical activity: Exercise can help improve blood circulation and reduce pelvic pain. Exercise also helps regulate weight, which has a positive effect on fibroids.
• Use of iron supplements: In case of severe bleeding, it is recommended to take iron supplements with the doctor’s advice to prevent anemia.
• Stress management: Stress can affect hormonal balance. Yoga exercises, meditation and deep breathing techniques can help reduce stress.
New medical perspective in the treatment of uterine fibroids
In recent years, new research has been conducted on new treatments for uterine fibroids, some of which include:
1. Non-surgical methods such as HYFU (HIFU): This method uses high-frequency sound waves to destroy fibroids without the need for surgery.
2. Newer drugs: Newer hormone blocking drugs are being investigated to reduce the size of fibroids.
3. Limited radiotherapy: using more precise methods in radiotherapy in order to reduce side effects and direct destruction of fibroids.
Summary and general recommendations
Uterine fibroids are generally benign and in many cases remain untreated.
For women with severe symptoms or fertility concerns, there are a variety of treatments that can help improve the condition.
Performing regular examinations, following a healthy diet, paying attention to self-care and receiving medical advice are the best strategies for managing and controlling fibroids.
Due to the advances in treatment and care, the possibility of enjoying a quality life has increased for women with uterine fibroids.