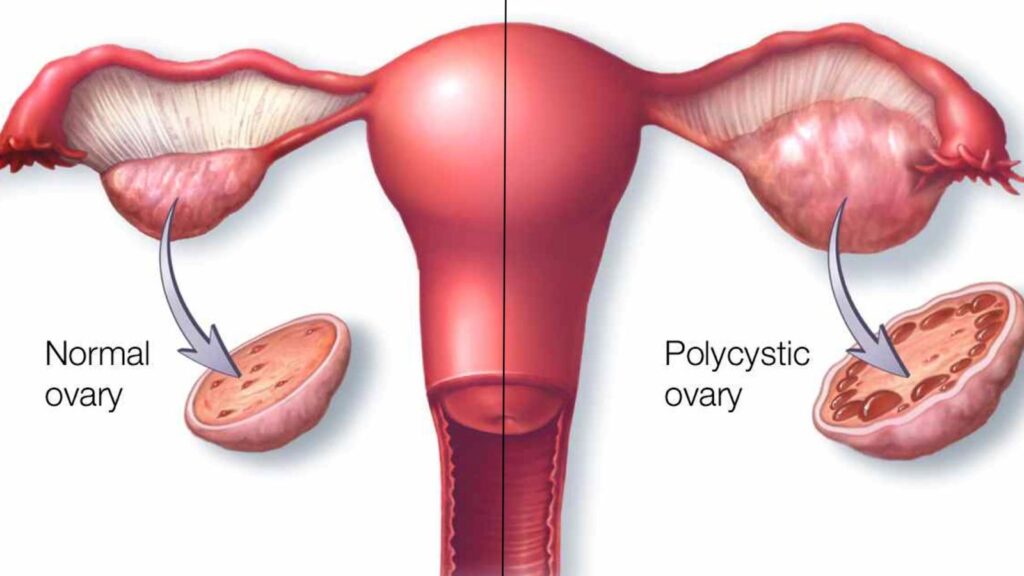
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or polycystic ovary syndrome is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age that occurs due to hormonal imbalance in the body.
This disorder can cause numerous small cysts in the ovaries, ovulation disorder and various other symptoms.
The exact cause of this syndrome has not yet been fully determined, but genetic factors and insulin resistance are among the factors that contribute to its occurrence.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person and include the following:
1. Irregular periods: Ovulation disorder causes women with this syndrome to have irregular periods. These people may have long intervals between periods or even have amenorrhea.
2. Weight gain and obesity: Many women with PCOS experience weight gain and obesity, especially in the abdominal area, which can lead to aggravation of symptoms.
3. Increased male hormones (androgens): This disorder increases the level of male hormones in the body,
which can cause symptoms such as excessive hair growth (in areas such as the face and body), acne, and male pattern baldness.
4. Ovarian cysts: In women with PCOS, the ovaries may contain numerous small cysts that form due to the lack of release of eggs and their accumulation in the ovary.
5. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which means the body does not respond well to insulin,
which can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. .
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully known, but the following factors can contribute to its occurrence:
• Genetics: Genetic factors can be effective in the occurrence of PCOS, and if a person’s family member (such as mother or sister) has this syndrome, the probability of having it increases.
• Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is seen in many women with PCOS, which increases the level of insulin in the blood and produces more male hormones.
• Hormonal disorders: an increase in the level of androgen, insulin and loptin hormones may disrupt the hormonal balance and lead to the occurrence of this syndrome.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
PCOS treatment is usually based on the individual’s symptoms and needs and includes the following:
1. Changes in lifestyle: losing weight and maintaining a suitable weight, doing regular exercise and eating healthy can help reduce symptoms and improve the condition of patients.
2. Medications: Taking medications such as birth control pills to regulate hormones and control periods, metformin to reduce insulin resistance,
and anti-androgen medications to reduce hair loss and acne.
3. Fertility treatments: For women who want to get pregnant, drugs are prescribed to stimulate ovulation.
4. Diabetes management: If a person has diabetes, controlling blood sugar and using diabetes medications can help manage symptoms.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a chronic disease and requires long-term management and care. Consulting a specialist doctor
and following the recommended treatments can help improve the symptoms and reduce the complications of this syndrome.
Next, in addition to the treatment methods mentioned, paying attention to some points can help in better management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS):
The importance of nutritional changes
Proper nutrition is one of the most important ways to manage PCOS symptoms. Some nutritional recommendations that can help improve this syndrome include:
1. Low-carb and low-sugar diet: Reducing the consumption of sugars and simple carbohydrates can help control insulin levels and improve insulin resistance.
Eating foods with a low glycemic index, such as vegetables, whole grains, and healthy proteins, helps improve blood sugar.
2. Increasing fiber in the diet: Consuming foods rich in fiber such as fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains can help control blood sugar and reduce the feeling of hunger.
3. Healthy fats: Healthy fats such as omega-3 found in fish, avocados, and olive oil help reduce inflammation in the body and improve overall health.
4. Avoiding processed foods: Eating processed foods and fast foods can increase blood sugar and unhealthy fats in the body, which aggravates the condition of PCOS.
Stress management
Stress can aggravate the symptoms of PCOS because it increases the level of the hormone cortisol (stress hormone) and can negatively affect the hormonal balance.
Mental exercises such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing and even enough sleep can be effective in reducing stress and improving the condition of patients.

Sports exercises
Regular and appropriate exercise, especially aerobic and resistance exercises (such as walking, swimming, weight lifting, and cycling)
help control weight, reduce insulin resistance, and improve cardiovascular health.
Exercise also reduces the level of male hormones and improves hormonal function.
Regular medical follow-ups
Given that PCOS can be associated with other problems such as diabetes, heart problems, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol,
regular follow-ups with your doctor to check your health are especially important. Also, regular control of blood sugar,
blood pressure and cholesterol level is recommended in patients with this syndrome.
The importance of psychological support and counseling
In addition to physical problems, PCOS can also have psychological effects, including reduced self-confidence, stress, and even depression.
Support from family and friends, consultation with a psychologist or specialist counselor, and participation in patient support groups can help reduce the psychological effects of this syndrome.
In general, polycystic ovary syndrome does not have a definitive cure, but with changes in lifestyle, proper nutrition and follow-up of medical treatments,
symptoms can be controlled and the development of possible complications can be prevented.
Long-term complications of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
If polycystic ovary syndrome is not managed properly, it can cause long-term complications, including:
1. Fertility problems: One of the most common complications of PCOS is fertility problems.
Failure to ovulate can decrease the chance of pregnancy, and if pregnancy occurs, the risk of miscarriage may increase.
2. Type 2 diabetes: Women with PCOS are more at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance, which is common in this syndrome,
can increase blood sugar and eventually lead to diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular diseases: PCOS can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Obesity, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels can lead to heart problems.
4. Uterine cancer: lack of regular ovulation can increase the risk of uterine cancer (endometrium).
This problem arises due to the accumulation and non-discharge of endometrial tissue over time.
5. Sleep disorders: Some women with PCOS may experience sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, which can lead to other health problems.
6. Psychological problems: The psychological effects of PCOS include anxiety, depression and low self-confidence.
Appearance changes caused by excess hair and skin problems may affect a person’s mood.
Key tips for managing PCOS
For the effective management of polycystic ovary syndrome, paying attention to the following points can be useful:
1. Awareness of symptoms: Knowing the signs and symptoms of PCOS helps women to consult a doctor in time and prevent complications.
2. Avoiding self-medication: Women should avoid self-medication and the use of non-prescription drugs without consulting a doctor.
Treatment should be done under the supervision of a specialist and based on individual conditions.
3. Paying attention to mental health: Maintaining mental health and referring to psychological specialists when needed will help reduce the negative effects of PCOS.
4. Join support groups: Joining support groups can help people share their experiences with others and get advice from each other.
5. Use of technology: Some special programs and applications can help women to track their menstrual cycle, symptoms and weight changes and thus have a better management of PCOS.
conclusion
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a complex disorder that requires regular management and treatment.
By being aware of the symptoms, changing lifestyle, using medical treatments and social support,
women can help improve their quality of life and minimize the complications caused by this syndrome.
Consulting with a specialist doctor and following appropriate treatments can help control symptoms and improve health.
The cause of polycystic ovary syndrome (ovarian laziness) is not completely known, but several factors may contribute to its occurrence. These factors include the following:
1. Genetic factors
Research shows that genetic factors can play a role in PCOS. If a family member such as mother or sister is suffering from this syndrome, the probability of getting it increases.
2. Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is one of the key factors in PCOS. In this condition, the body does not respond well to insulin,
which can lead to increased levels of insulin and androgen hormones (male hormones).
This issue can have effects on ovulation and menstrual cycle.
3. Hormonal disorders
In PCOS, the level of male hormones (androgens) in women’s bodies increases, which can cause symptoms such as acne, hair loss, and ovulation problems.
Also, hormonal imbalance can affect the menstrual cycle.
4. inflammation
Research suggests that chronic inflammation may play a role in PCOS. This inflammation can lead to insulin resistance and increased levels of androgen hormones.
5. Environmental factors
Environmental and lifestyle factors can also affect the incidence of PCOS.
Improper diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity are among the factors that can increase the risk of developing this syndrome.
6. Hormonal changes during puberty
Hormonal changes during puberty and hormonal changes at certain times such as menstruation and pregnancy can also affect the occurrence of PCOS.
conclusion
In general, a combination of genetic, hormonal and environmental factors can be effective in polycystic ovary syndrome.
Considering that this syndrome has wide effects on the physical and mental health of women, its timely diagnosis and correct management are very important.
Consultation with a specialist doctor can help to better understand this disease and choose the appropriate treatment methods.

Effects and complications of ovarian laziness
PCOS can cause many complications for women. These complications include the following:
1. Fertility problems
PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility in women. Not ovulating regularly means a reduced chance of pregnancy.
Women with PCOS may also experience problems such as frequent miscarriages.
2. Type 2 diabetes
Women with PCOS are more prone to type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance, which is commonly seen in this syndrome, can lead to elevated blood sugar levels.
3. Cardiovascular problems
The risk of cardiovascular diseases is higher in women with PCOS. Obesity, high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels can lead to these problems.
4. uterine cancer
Women with PCOS who have irregular periods may be at a higher risk of developing uterine cancer.
Accumulation of endometrial tissue due to lack of regular ovulation can lead to this complication.
5. mental problems
Ovarian laziness can have profound psychological effects. Many women with PCOS may experience anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Appearance changes caused by symptoms such as excess hair and acne can affect a person’s mood.
6. sleep disorders
Some women with PCOS may experience sleep disorders such as sleep apnea. These disorders can negatively affect the quality of life and general health.
Management and treatment of ovarian indolence
Management and treatment of ovarian laziness requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some ways to manage this syndrome:
1. Lifestyle changes
• Healthy eating: following a balanced and low-carbohydrate diet can help control blood sugar and lose weight. Consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains and healthy proteins is recommended.
• Regular exercise: Regular physical activity helps to lose weight and improve insulin sensitivity. A combination of aerobic and resistance exercises can be effective.
2. Medicines
• Birth control pills: These drugs can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the level of androgen hormones.
• Metformin: This drug is usually prescribed to control blood sugar and reduce insulin resistance.
• Anti-androgen drugs: These drugs can help reduce hair loss and improve acne.
3. Psychological counseling
Counseling with a psychologist can be helpful in managing the psychological and emotional effects of PCOS.
Social support and participation in support groups can also help reduce stress and anxiety.
4. Medical follow-ups
Patients with PCOS should consult their doctor regularly to monitor their health and prevent possible complications.
conclusion
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common and complex disorder that requires regular management and treatment.
By knowing the symptoms and factors affecting this syndrome, women can take measures to improve their quality of life.
Consulting with a specialist doctor and choosing appropriate treatments can help control symptoms and prevent complications.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or ovarian indolence can be characterized by a set of clinical symptoms that vary from woman to woman.
Clinical symptoms of this disorder usually include the following:
1. Menstrual disorders
• Irregular menstruation: One of the most common symptoms of PCOS is irregular menstruation.
Women with this syndrome may have long intervals between periods or experience amenorrhea.
• Light or heavy periods: Some women may have very light or heavy periods.
2. Weight gain and obesity
• Central obesity: Many women with PCOS experience weight gain and obesity, especially in the abdominal area.
This situation can lead to the aggravation of symptoms and complications related to this syndrome.
3. Hormonal symptoms
• Increase in androgen hormones: An increase in the level of male hormones (androgens) in the body can lead to symptoms such as:
o Excess hair: abnormal growth of hair in areas such as the face, chest, abdomen and back.
o Acne: Occurrence of acne and skin problems caused by hormonal imbalance.
o Male pattern baldness: reduction of head hair and sudden hair loss.
4. Fertility problems
• Infertility: lack of regular ovulation can lead to reduced chances of pregnancy. Many women with PCOS have fertility problems.
5. Metabolic problems
• Insulin resistance: This condition can lead to an increase in blood sugar and the risk of type 2 diabetes.
• Blood lipid disorders: Increased levels of blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) may be observed in women with PCOS.
6. Psychiatric symptoms
• Depression and anxiety: Women with PCOS may face psychological problems such as anxiety and depression.
These symptoms can be due to hormonal changes and the physical effects caused by the syndrome.
7. sleep problems
• Sleep disorders: Some women with PCOS may experience sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
8. Other symptoms
• Changes in the skin: the skin may become darker or have brown spots and color changes.
• Pain in the pelvic area: Some women may feel pain in the pelvic area, which may be caused by ovarian cysts.
conclusion
Timely and correct diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome clinical symptoms is very important.
This disorder can have profound effects on the quality of life and general health of women.
If you see any of these symptoms, it is necessary to consult a specialist doctor to provide appropriate solutions for management and treatment.